box plot with normal distribution A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary . At Union Made Stickers, we not only believe in union made products, we ARE union. .
0 · skewed to the right boxplot
1 · positively skewed distribution box plot
2 · positively skewed box plots
3 · positive skew vs negative boxplot
4 · how to interpret boxplot results
5 · boxplot skewed to the left
6 · box and whiskers chart explained
7 · 25th percentile on a boxplot
UMC .22 Short box. Note the box is the same style as the Union Metallic Cartridge & Cap Company box and also still has Made under Patent of Smith & Wesson. Box is two-piece
A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset.
A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary .
skewed to the right boxplot
positively skewed distribution box plot
Box plots are used to show distributions of numeric data values, especially when you want to compare them between multiple groups. They are built to provide high-level information at a .Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left, or skewed to the right, and estimate the .One way to understand a box plot is to think of what a box plot of data from a normal distribution will look like. The graph below shows a standard normal probability density function ruled into four quartiles, and the box plot you would . A boxplot is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of data based on a five number summary (“minimum”, first quartile (Q1), median, third quartile (Q3), and “maximum”). .
Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median.Normal Distribution : If a box plot has equal proportions around the median, we can say distribution is symmetric or normal. Positively Skewed : For a distribution that is positively skewed, the box plot will show the median closer to the lower . The following plot shows a boxplot of data with a normal distribution and a box plot of data with a log normal distribution. The plots show that the distribution between the data points is different. Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.
A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset.A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], median, third quartile [Q3] and “maximum.”Box plots are used to show distributions of numeric data values, especially when you want to compare them between multiple groups. They are built to provide high-level information at a glance, offering general information about a group of .
Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left, or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median.One way to understand a box plot is to think of what a box plot of data from a normal distribution will look like. The graph below shows a standard normal probability density function ruled into four quartiles, and the box plot you would expect if you took a very large sample from that distribution. A boxplot is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of data based on a five number summary (“minimum”, first quartile (Q1), median, third quartile (Q3), and “maximum”). It can tell you about your outliers and what their values are.
Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median.Normal Distribution : If a box plot has equal proportions around the median, we can say distribution is symmetric or normal. Positively Skewed : For a distribution that is positively skewed, the box plot will show the median closer to the lower or bottom quartile. The following plot shows a boxplot of data with a normal distribution and a box plot of data with a log normal distribution. The plots show that the distribution between the data points is different. Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.
positively skewed box plots
A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset.A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], median, third quartile [Q3] and “maximum.”Box plots are used to show distributions of numeric data values, especially when you want to compare them between multiple groups. They are built to provide high-level information at a glance, offering general information about a group of .Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left, or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median.
One way to understand a box plot is to think of what a box plot of data from a normal distribution will look like. The graph below shows a standard normal probability density function ruled into four quartiles, and the box plot you would expect if you took a very large sample from that distribution. A boxplot is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of data based on a five number summary (“minimum”, first quartile (Q1), median, third quartile (Q3), and “maximum”). It can tell you about your outliers and what their values are.
Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median.
Normal Distribution : If a box plot has equal proportions around the median, we can say distribution is symmetric or normal. Positively Skewed : For a distribution that is positively skewed, the box plot will show the median closer to the lower or bottom quartile.
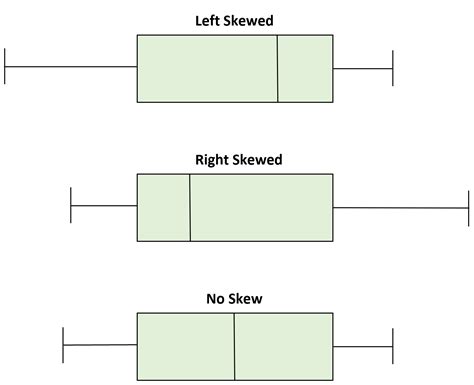
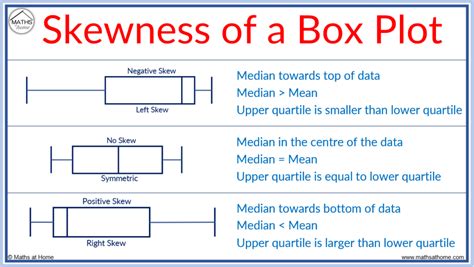
positive skew vs negative boxplot

how to interpret boxplot results
boxplot skewed to the left
box and whiskers chart explained
Connect multiple fountain lights to a single power supply with these bronze junction boxes; Eight side ports; 1" FTP bottom inlet; Overall dimensions are 6 3/4" diameter x 2" tall with compression seals; Body dimensions are 5 3/4" .
box plot with normal distribution|boxplot skewed to the left