a gravity flow distribution box requires Gravity distribution is the conveyance of effluent from a distribution box through the percolation lines at less than full flow conditions. Flow to the initial distribution box may be . $12.91
0 · septic tank distribution box diagram
1 · distribution box definition
Sigma's weatherproof closure plugs help keep moisture from the electrical wiring by closing unused holes in weatherproof boxes, extension rings or covers. In a world that runs largely on electricity, junction boxes are crucial to protecting electrical wiring systems.
Gravity flow distribution considers siphons, distribution boxes and headers. Refer to Appendix II for diagrams illustrating flow splitting configurations. A siphon is a method of providing a volume-based dose to the leaching bed as an alternative to a pump that does not require any . Gravity distribution is the conveyance of effluent from a distribution box through the percolation lines at less than full flow conditions. Flow to the initial distribution box may be .The distribution box is a container that accepts effluent and distributes the effluent evenly to one or more trenches in the absorption field. In some cases gravity flow from the septic tank to the .gravity flow, dosed to distribution cell or distribution box, then applied by gravity flow to the distribution cell, or by use of pressure distribution, unless pressure distribution is required in .
A frequently used, simple method for distributing effluent is gravity flow. Gravity flow allows wastewater to flow by gravity through large diameter pipes into the subsurface soil absorption Design specifications & regulations for the D-box and septic effluent distribution/disposal: These model septic design regulations discusses the means of distribution or movement of effluent from the septic tank to the absorption . Gravity-Flow Distribution • Appropriate for deep, well-drained sites • Most widely used • Least expensive • Typically 4” Pipe • Does not distribute effluent uniformly regardless of .Gravity distribution: key design objectives Uniform distribution needs to achieve 2 essential objectives: #1: LATERAL DISTRIBUTION • Distribution of effluent over the width of the system .
Gravity distribution is the conveyance of effluent from a distribution box through the percolation lines at less than full flow conditions. Flow to the initial distribution box may be initiated by .Gravity flow distribution considers siphons, distribution boxes and headers. Refer to Appendix II for diagrams illustrating flow splitting configurations. A siphon is a method of providing a volume-based dose to the leaching bed as an alternative to a .Gravity distribution is the conveyance of effluent from a distribution box through the percolation lines at less than full flow conditions. Flow to the initial distribution box may be initiated by pump, siphon or gravity.The distribution box is a container that accepts effluent and distributes the effluent evenly to one or more trenches in the absorption field. In some cases gravity flow from the septic tank to the absorption field is not feasible and a dosing tank is necessary.
septic tank distribution box diagram
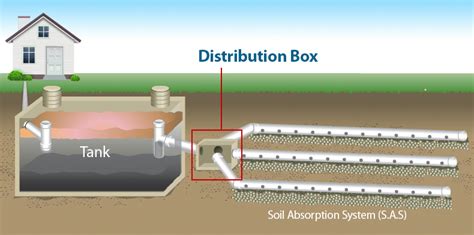
Gravity systems typically use a distribution box (d-box) to equally distribute the wastewater into each lateral pipe in the drainfield. Once the wastewater reaches the lateral pipes, it flows out of small holes into a gravelled trench eventually reaching the surrounding soil.
gravity flow, dosed to distribution cell or distribution box, then applied by gravity flow to the distribution cell, or by use of pressure distribution, unless pressure distribution is required in accordance with s. SPS 383.44 (5) (b) 2. If DWF ≥ 1500 gpd, effluent must be dosed toA frequently used, simple method for distributing effluent is gravity flow. Gravity flow allows wastewater to flow by gravity through large diameter pipes into the subsurface soil absorption
Design specifications & regulations for the D-box and septic effluent distribution/disposal: These model septic design regulations discusses the means of distribution or movement of effluent from the septic tank to the absorption system or leach field. Gravity-Flow Distribution • Appropriate for deep, well-drained sites • Most widely used • Least expensive • Typically 4” Pipe • Does not distribute effluent uniformly regardless of media type –Drops effluent in one or two locationsGravity distribution: key design objectives Uniform distribution needs to achieve 2 essential objectives: #1: LATERAL DISTRIBUTION • Distribution of effluent over the width of the system (in each lateral or trenches) #2: LONGITUDINAL (length wise) DISTRIBUTION • Distribution of effluent over the length of the system.Gravity distribution is the conveyance of effluent from a distribution box through the percolation lines at less than full flow conditions. Flow to the initial distribution box may be initiated by pump, siphon or gravity.
distribution box definition
Gravity flow distribution considers siphons, distribution boxes and headers. Refer to Appendix II for diagrams illustrating flow splitting configurations. A siphon is a method of providing a volume-based dose to the leaching bed as an alternative to a .
Gravity distribution is the conveyance of effluent from a distribution box through the percolation lines at less than full flow conditions. Flow to the initial distribution box may be initiated by pump, siphon or gravity.The distribution box is a container that accepts effluent and distributes the effluent evenly to one or more trenches in the absorption field. In some cases gravity flow from the septic tank to the absorption field is not feasible and a dosing tank is necessary.
rapid prototyping sheet metal
Gravity systems typically use a distribution box (d-box) to equally distribute the wastewater into each lateral pipe in the drainfield. Once the wastewater reaches the lateral pipes, it flows out of small holes into a gravelled trench eventually reaching the surrounding soil.gravity flow, dosed to distribution cell or distribution box, then applied by gravity flow to the distribution cell, or by use of pressure distribution, unless pressure distribution is required in accordance with s. SPS 383.44 (5) (b) 2. If DWF ≥ 1500 gpd, effluent must be dosed to
A frequently used, simple method for distributing effluent is gravity flow. Gravity flow allows wastewater to flow by gravity through large diameter pipes into the subsurface soil absorption Design specifications & regulations for the D-box and septic effluent distribution/disposal: These model septic design regulations discusses the means of distribution or movement of effluent from the septic tank to the absorption system or leach field. Gravity-Flow Distribution • Appropriate for deep, well-drained sites • Most widely used • Least expensive • Typically 4” Pipe • Does not distribute effluent uniformly regardless of media type –Drops effluent in one or two locations
Gravity distribution: key design objectives Uniform distribution needs to achieve 2 essential objectives: #1: LATERAL DISTRIBUTION • Distribution of effluent over the width of the system (in each lateral or trenches) #2: LONGITUDINAL (length wise) DISTRIBUTION • Distribution of effluent over the length of the system.

Sigma's weatherproof two-gang boxes provide a junction for conduits and can house up to two wired devices such as a receptacle or switch. The rugged, die-cast construction prevents moisture penetration making the boxes suitable for wet, damp or dry locations.
a gravity flow distribution box requires|septic tank distribution box diagram