box plot symmetric distribution To determine whether a distribution is skewed in a box plot, look at where the median line falls within the box and whiskers. You have a symmetrical distribution when the box centers approximately on the median line, and the upper and . Special-order, delivery services, cutting services and more! Order what you need, when you need it – from one piece to a thousand! We buy it right, so we can sell it right! CONTACT US TODAY!
0 · understanding box plots for dummies
1 · skewed right graph box plot
2 · right skewed box plot vertical
3 · positively skewed box plots
4 · positive skew vs negative boxplot
5 · left skewed box plot vertical
6 · boxplot skewed right or left
7 · box plot negatively skewed
A junction box is not a special type of box but any standard electrical box used to enclose wire splices. The most commonly used box for junctions is a 4-inch square box (either metal or strong plastic), which offers ample space for making wire connections with multiple wires or .
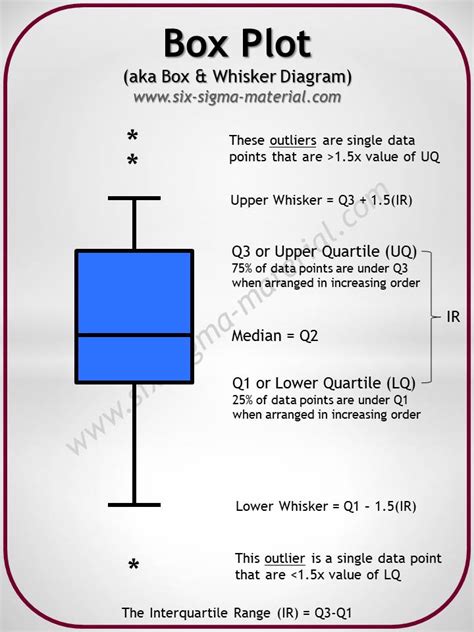
Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed .To determine whether a distribution is skewed in a box plot, look at where the median line falls within the box and whiskers. You have a symmetrical distribution when the box centers approximately on the median line, and the upper and .The box plot distribution will explain how tightly the data is grouped, how the data is skewed, and also about the symmetry of data. Positively Skewed: If the distance from the median to the maximum is greater than the distance from .
When the median is in the middle of the box and the whiskers are roughly equal on each side, the distribution is symmetrical (or “no” skew). The following examples illustrate how to use box plots to determine if a distribution .When a data distribution is symmetric, you can expect the median to be in the exact center of the box: the distance between Q1 and Q2 should be the same as between Q2 and Q3. Outliers .Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed .
Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left, or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median.Symmetric Data. A symmetric distribution with its corresponding box plot: A symmetric boxplot with distribution curve.
Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median. The box plot shape will show if a statistical data set is normally distributed or skewed. When the median is in the middle of the box, and the whiskers are about the same on both sides of the box, then the distribution is symmetric.Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed right.
understanding box plots for dummies
To determine whether a distribution is skewed in a box plot, look at where the median line falls within the box and whiskers. You have a symmetrical distribution when the box centers approximately on the median line, and the upper and lower whiskers are about equal length.The box plot distribution will explain how tightly the data is grouped, how the data is skewed, and also about the symmetry of data. Positively Skewed: If the distance from the median to the maximum is greater than the distance from the median to the minimum, then the box plot is positively skewed. When the median is in the middle of the box and the whiskers are roughly equal on each side, the distribution is symmetrical (or “no” skew). The following examples illustrate how to use box plots to determine if a distribution is right-skewed, left-skewed, or has no skew.When a data distribution is symmetric, you can expect the median to be in the exact center of the box: the distance between Q1 and Q2 should be the same as between Q2 and Q3. Outliers should be evenly present on either side of the box.
Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed right.Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left, or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median.
Symmetric Data. A symmetric distribution with its corresponding box plot: A symmetric boxplot with distribution curve.
Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median. The box plot shape will show if a statistical data set is normally distributed or skewed. When the median is in the middle of the box, and the whiskers are about the same on both sides of the box, then the distribution is symmetric.Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed right.
To determine whether a distribution is skewed in a box plot, look at where the median line falls within the box and whiskers. You have a symmetrical distribution when the box centers approximately on the median line, and the upper and lower whiskers are about equal length.The box plot distribution will explain how tightly the data is grouped, how the data is skewed, and also about the symmetry of data. Positively Skewed: If the distance from the median to the maximum is greater than the distance from the median to the minimum, then the box plot is positively skewed.
When the median is in the middle of the box and the whiskers are roughly equal on each side, the distribution is symmetrical (or “no” skew). The following examples illustrate how to use box plots to determine if a distribution is right-skewed, left-skewed, or has no skew.When a data distribution is symmetric, you can expect the median to be in the exact center of the box: the distance between Q1 and Q2 should be the same as between Q2 and Q3. Outliers should be evenly present on either side of the box.
skewed right graph box plot
Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed right.Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left, or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median.Symmetric Data. A symmetric distribution with its corresponding box plot: A symmetric boxplot with distribution curve.

cnc machine control unit
cnc machine custom stamps
Metal Wholesale boasts a vast catalog including panels, trims, fasteners, and accessories – everything you need to bring your metal roofing or siding project to life. Wasting time with unresponsive suppliers or battling order mistakes slows you down.
box plot symmetric distribution|boxplot skewed right or left